From top to bottom is:
The I-V Characteristic for a Metallic Conductor
The I-V Characteristic for a Filament Lamp
The I-V Characteristic for a Thermistor
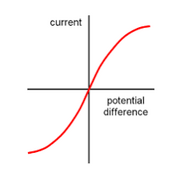
The I-V Characteristic for a Diode


The Resistivity of a metal increases with Temperature
-Charge is carried through metals by free electrons in a lattice of positive ions.
-Heating up the metal makes the more ion lattice vibration, which makes it harder for electrons to move.
-There are more collision between ions and electrons, more KE is transferred into other forms.
-When KE is lost, that means the drift velocity of electrons decreases, I=nqvA, the current decreases, which means the resistance increases.
As Temperature increases, more atoms have enough energy to release a free electron. -So there are more charge carriers. -Current (flow of electrons) is increased -Resistance decreases
